1. question: 修剪二叉搜索树(中等)
给你二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,同时给定最小边界low 和最大边界 high。通过修剪二叉搜索树,使得所有节点的值在[low, high]中。修剪树 不应该 改变保留在树中的元素的相对结构 (即,如果没有被移除,原有的父代子代关系都应当保留)。 可以证明,存在 唯一的答案 。
所以结果应当返回修剪好的二叉搜索树的新的根节点。注意,根节点可能会根据给定的边界发生改变。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/trim-a-binary-search-tree
示例 1:
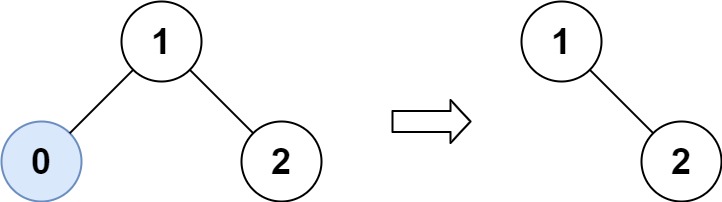
1
2
| 输入:root = [1,0,2], low = 1, high = 2
输出:[1,null,2]
|
示例 2:
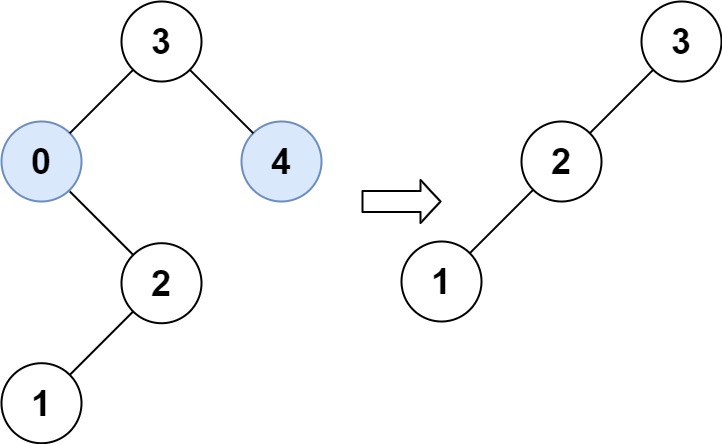
1
2
| 输入:root = [3,0,4,null,2,null,null,1], low = 1, high = 3
输出:[3,2,null,1]
|
提示:
1
2
3
4
5
| 树中节点数在范围 [1, 104] 内
0 <= Node.val <= 104
树中每个节点的值都是 唯一 的
题目数据保证输入是一棵有效的二叉搜索树
0 <= low <= high <= 104
|
2. answers
这道题和删除二叉搜索树中的节点类似,只不过上道题是只删除一个节点,需要重构。而这道题删除的是区间,因为二叉搜索树的节点之间有大小关系,所以如果某个节点不满足要求,那么它的左子树或者右子树也一定不满足要求。
- 如果节点小于区间,那么该节点的左子树也一定不满足要求。此时将该节点以及左子树删除,保留其右子树。即右子树的根节点代替当前节点。
- 如果节点大于区间,那么该节点的右子树也一定不满足要求。此时将该节点以及右子树删除,保留其左子树。即左子树的根节点代替当前节点。
因此,在遍历的时候,仍然需要保留当前节点的父节点。注意删除当前节点后,当前节点的变化,以及当前节点的父节点变化。先序迭代的代码如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
| public class Solution_0075 {
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
TreeNode head = new TreeNode(root.val, null, root);
root = head;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode pre = head;
while(root != null || stack.size() > 0) {
if(root == null) {
root = stack.pop();
pre = stack.pop();
}
if(root.right != null) {
stack.push(root);
stack.push(root.right);
}
if(root.val < low) {
if(pre.left == root) pre.left = root.right;
if(pre.right == root) pre.right = root.right;
root = root.right;
} else if(root.val > high) {
if(pre.left == root) pre.left = root.left;
if(pre.right == root) pre.right = root.left;
root = root.left;
}
else {
pre = root;
root = root.left;
}
}
return head.right;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeNode tn4 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode tn3 = new TreeNode(4);
TreeNode tn2 = new TreeNode(1, null, tn4);
TreeNode tn1 = new TreeNode(3, tn2, tn3);
Solution_0075 s = new Solution_0075();
TreeNode result = s.trimBST(tn1, 3, 4);
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(result);
while(queue.size() > 0 ) {
int length = queue.size();
while(length-- > 0) {
result = queue.poll();
System.out.print(result.val + "\t");
if(result.left != null) queue.offer(result.left);
if(result.right != null) queue.offer(result.right);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
|
3. 备注
参考力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台 (leetcode-cn.com),代码随想录 (programmercarl.com)。



