1. question: 链表相交(简单)
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交:
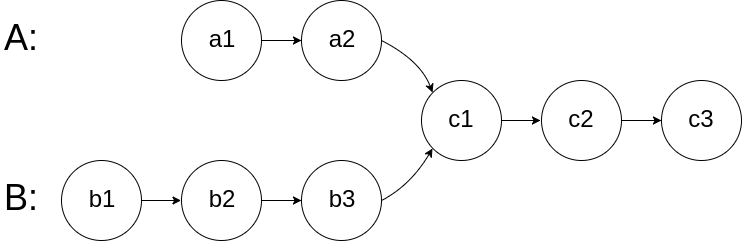
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci
示例 1:
1
2
3
4
5
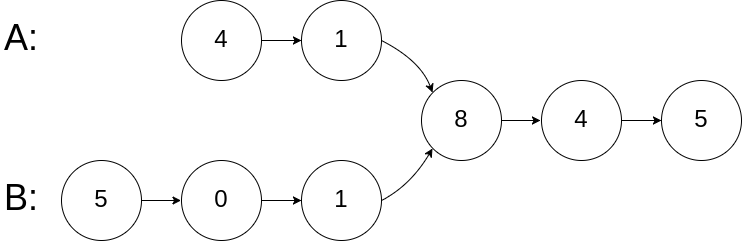
| 输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Intersected at '8'
解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
|
示例 2:
1
2
3
4
5
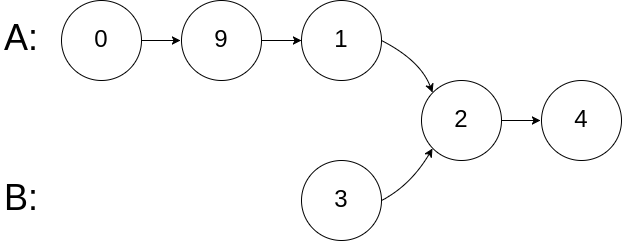
| 输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Intersected at '2'
解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
|
示例 3:
1
2
3
4
5
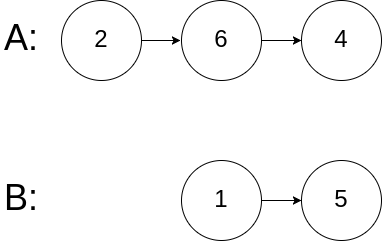
| 输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。
由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。
|
提示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| listA 中节点数目为 m
listB 中节点数目为 n
0 <= m, n <= 3 * 104
1 <= Node.val <= 105
0 <= skipA <= m
0 <= skipB <= n
如果 listA 和 listB 没有交点,intersectVal 为 0
如果 listA 和 listB 有交点,intersectVal == listA[skipA + 1] == listB[skipB + 1]
|
2. answers
这道题首先想到的是,先遍历一条链表,将链表中的节点存储到HashMap中。之后遍历另一条链表,并检索哈希表是否包含当前节点,如包含,则当前节点就是相交节点。
代码如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| public class Solution_0038 {
public static ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
HashMap<ListNode, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
boolean flag = true;
int index = 0;
while(headA != null) {
hashMap.put(headA, index);
headA = headA.next;
index ++;
}
while(headB != null) {
Integer integer = hashMap.get(headB);
if(integer != null) {
flag = false;
break;
} else {
headB = headB.next;
}
}
return !flag ? headB : null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println();
ListNode ln1 = new ListNode(4);
ListNode ln2 = new ListNode(6, ln1);
ListNode ln3 = new ListNode(2, ln2);
ListNode ln4 = new ListNode(5);
ListNode ln5 = new ListNode(1, ln4);
ListNode intersectionNode = getIntersectionNode(ln3, ln5);
System.out.println(intersectionNode);
}
}
|
怎么说呢,上面的方法还行吧,哈希表的检索效率也挺高的。这里参考博客尝试另一种方法。我们知道,链表中的节点只有一个后缀节点,那么只要相交,就不会再分开。所以说,相交的节点一定是结尾的几个节点。换句话说,就是结尾的节点一定是一一对应的,如果相同,则相交,如果不同则不相交。那么怎么同时遍历两个链表的结尾的几个节点呢?
其实就是遍历较短的链表的全部节点。可以先遍历两条链表,计算出链表长度。然后将长链表遍历,直到剩余节点个数和短链表的长度一样,然后再一起遍历。
代码如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
| public class Solution_0038_02 {
public static ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode newHeadA = headA, newHeadB = headB;
int lengthA = 0, lengthB = 0;
while(newHeadA != null) {
lengthA += 1;
newHeadA = newHeadA.next;
}
while(newHeadB != null) {
lengthB += 1;
newHeadB = newHeadB.next;
}
if(lengthA > lengthB) {
newHeadA = headA;
newHeadB = headB;
} else {
newHeadA = headB;
newHeadB = headA;
}
int sum = Math.abs(lengthA - lengthB);
while(sum > 0) {
newHeadA = newHeadA.next;
sum--;
}
while(newHeadA != null) {
if(newHeadA == newHeadB) {
return newHeadA;
} else {
newHeadA = newHeadA.next;
newHeadB = newHeadB.next;
}
}
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println();
ListNode ln1 = new ListNode(5);
ListNode ln2 = new ListNode(4, ln1);
ListNode ln3 = new ListNode(8, ln2);
ListNode ln4 = new ListNode(1, ln3);
ListNode lnA = new ListNode(4, ln4);
ListNode ln6 = new ListNode(1, ln3);
ListNode ln7 = new ListNode(0, ln6);
ListNode lnB = new ListNode(5, ln7);
ListNode intersectionNode = getIntersectionNode(lnA, lnB);
System.out.println(intersectionNode.val);
}
}
|
3. 备注
参考力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台 (leetcode-cn.com),代码随想录 (programmercarl.com)。





